In geometry, a triangle has 4 different triangle centers: the centroid, circumcenter, orthocenter, and incenter.
Incenter of a Triangle
The incenter I is the center of the incircle for a polygon or insphere for a polyhedron (when they exist). The corresponding radius of the incircle or insphere is known as the inradius.The incenter can be constructed as the intersection of angle bisectors. It is also the interior point for which distances to the sides of the triangle are equal. It has trilinear coordinates 1:1:1.
The (interior) bisector of an angle, also called the internal angle bisector (Kimberling 1998, pp. 11-12), is the line or line segment that divides the angle into two equal parts.
Above Figure,
∠BIC = 90° + ∠A/2
∠AIC = 90° + ∠B/2
∠AIB = 90° + ∠C/2
Inradius of a Triangle
In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides. The center of the incircle is a triangle center called the triangle's incenter.Above Diagram where,
Inradius, r = 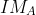 =
= 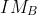 =
= 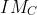
Inradius, r = 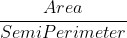
For Equilateral Triangle,
Inradius, r = h / 3
r = a / 2√3
For right triangle,
Inradius, r = 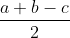 , where c is Hypotenuse
, where c is Hypotenuse
Circumcenter of a Triangle
Circumcenter is the point where the perpendicular bisectors (of sides) of a triangle intersect. The circumcenter is also the center of the triangle's circumcircle - the circle that passes through all three of the triangle's vertices. \
I'm denoting circum center - S and Imagine I'm drawing lines from S to each vertices.
Then,
∠BSC = 2 ∠A
∠ASC = 2 ∠B
∠ASB = 2 ∠C
Circum Radius of a Triangle
Circumradius, R = AS = BS = CS
Circumradius, R = 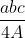
Where,
a,b,c : each sides of the triangle
A - Area of triangle.
For Equilateral Triangle,
Circumradius, R = 2h / 3
Circumradius, R = a / √3
For Right Triangle,
Circumradius, R = h/2
The position of Circumcenter in each triangle are:













In fact, this is the hardest part of the assignment but you were able to explain it clearly and in details. The provided figures are also understandable!
ReplyDelete